I’ve heard it thrown around in professional circles and how everybody’s doing it wrong, so… who actually does use it?
For smaller teams
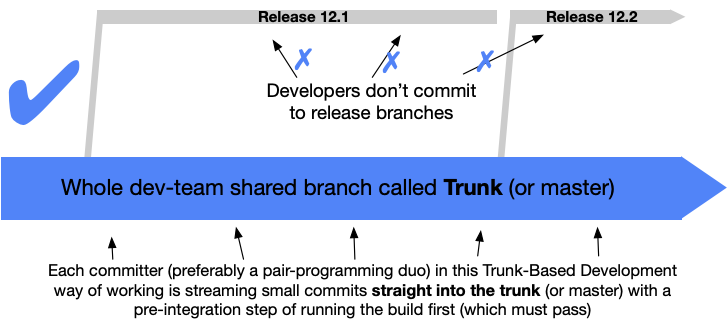
“scaled” trunk based development
Here there’s main. You branch off. Do your work. Make a PR to main. Build passes and someone approves, merge to main. Production release is done by tagging main.
The branches are short lived because the units of work we select are small. You have like one pr for an endpoint. You don’t wait until the entire feature with 20 endpoints is ready to merge.
Seems to work fine. I think this is different than trunk based development but honestly I’m not sure I understand trunk.
Seems to work fine. I think this is different than trunk based development but honestly I’m not sure I understand trunk.
Same. But it feels like you’re doing it.
This is enough for most projects.
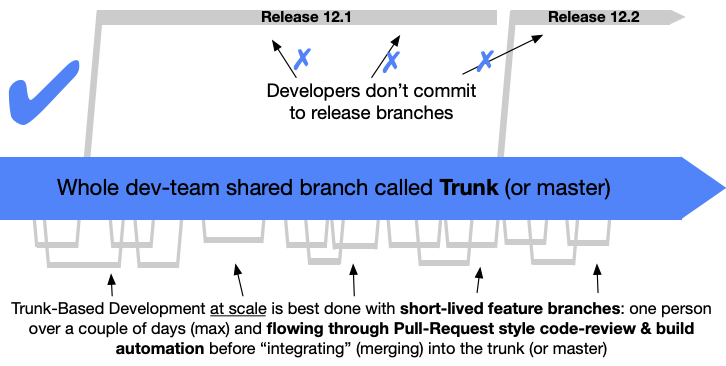
Second diagram, yes absolutely.
Short lived (1-2 day) branches, and a strong CI systems to catch regressions.
Be warned, the strength in the CI lies in its capacity to detect when some functionality that previously worked doesn’t work anymore. So, the flow must be green always, and it must evolve as the features evolve. Without good CI you’re destined for failure.
lies in its* capacity
I haven’t worked on any teams where all members committed “every 24 hours”, and there have always been some branches that live longer than we’d like (usually just unfinished work that got deprioritized but still kept as an eventual “todo”), but most teams I’ve worked on have indeed followed the basic pattern of only one long-lived branch, reviews and CI required prior to merge, and all feature-branches being short-lived.
A hard timeline on commit strikes me as less than ideal.
People are people. They have issues, they screw up, but they still write good code.
Seems like a brutal metric that encourages minimal commits without real change.
Yeah, agreed.
We’ve used the “scaled” approach for a whilen and we make tags to release. Every time we have a long-lived branch that isn’t main/master something gets fucked up or we spend an extra few days just to reconcile the conflicts. Luckily we’re service based so supporting multiple versions of a product is very rare.
I do, on a 900+ developer mono repo. Works like a charm.
We just have a CD that allows to deliver each project each micro service individually.
You deliver your software on CDs?
Most likely CD is intended to mean continuous delivery, which commonly means automation in processes that deliver your software to it’s target audience.
It does indeed ^^
Holy crap that’s a lot of devs 😳
Yeah, the biggest problem is keeping up to date.
That’s where the mono repo really shines. We have a folder for common stuff that everyone depends upon. A modification is automatically applied/compatible with every micro service. Really streamline the lib updates problem ^^
Out of curiosity, how long are CI and CD runs? And are there any particularities in the way of working for example every PR/MR is created by pair programmers, or the use of josh to cut down on time to clone, stuff like that.
Team of three. We do the feature branches, pull requests and code reviews. With the right culture, it keeps devs informed about the various projects and gives a nice space to discuss about the practice.
EDIT: we do automated linting and formatting checks too. Keeps things coherent.
I’ve been doing this for the past 10 years or so. When I joined my current company a few years ago, it was one of the first things I pushed for. It made cycle times go down drastically and value is being delivered to end users at a much higher rate now.
With enough tests and automation, there is almost no reason not do on the web. On embedded or mobile platforms this might be a bit more difficult, although not entirely impossible.
The use of feature toggles also greatly enhanced our trust in being able to turn a feature off again if it turned out to be faulty somehow. Although we usually opt for patching bugs, it gives the business as a whole more confidence.
Scaled trunk based all year long, every year, every team.
Life is too short to tolerate long-lived branches.
Not saying anything about good or bad, but trunk-based development doesn’t work when the business requires you to have multiple releases under development concurrently.
We don’t have release branches, the commit is just tagged as being currently deployed in production.
People merge their feature branches to master during working hours (by merging CI validated PRs) and release when they get a chance. Normally do about 10-20 releases per day.
I guess we do scaled trunk development, if you want to call it that. We do allow direct commits, for trivial or safe stuff where reviews would be more noise and hindrance than value. (Code formatting etc.)
We only have one current release version though. (And at times a current test version that deviates from it.)
If there’s a need to create a patch release for a tagged version when the trunk proceeded forward with something that shall not be included, I create only a temporary branch from the earlier tagged commit to tag (=create) that patch release.
What are the release branches supposed to be in your graphs? It says developers don’t commit. Then who does?
Those aren’t my graphs, there are from the link in the post. I’ve only once worked with release branches and it was a nightmare.
We do, for two 2-3 person projects, where no code reviews are done. This is mostly because (a) it’s “just” a rewrite and (b) most new functionality is small and well-defined. For bigger features a local branch is checked out and then merged back later. Commits are always up-to-date, which makes it much easier to test integration of new featues.
With git. Every time we start work, we pull. After every commit, we push (and pull/merge/rebase) if necessary.
Worked with both, both worked fine.
Different size companies, right?
Yes. We use SVN. I hate it. I’m trying to build a case to switch to git. We’re a small team, but a growing team
Welcome time traveler. If you’re able to return to your own timeline, buy some Apple stock.
/joking
But I hope your team does migrate. SVN is pretty bad, compared to git.
Do you really need to make a case? Does your company not trust devs? Is there people leading that have no idea about technology? SVN is dead. Many devs won’t touch it. It’s best way to say to new candidates your company is backwards. Many would refuse to work in a company that uses a version control system that has been dead 7 years.
It’s effort to switch, and we don’t benefit from having separate copies of the repo bc we’re so small. No one steps on eachother’s toes, so distributed version control isn’t necessary.
Now, the fact that most devs know git and SVN is dead is not lost on our CTO, but putting the effort to switch over doesn’t provide direct value to the customer, so I have to make the case that switching to git would do enough from a productivity and maintenance standard to effect customers.
But just productivity and maintenance but if your devs start to leave or retire, you’re not gonna get the best quality replacements for them if you’re using outdated tech. No one wants to learn new skills that aren’t going to help with their career growth.
I’m a relatively new hire and we just hired another person 2 weeks ago
My company still uses SVN, but we have almost 20 years of history in the repository, not including the autogenerated commits from when we migrated from CVS.
My department would like for us to move to git (some sub projects have) but it’s important for our process to retain the history and nobody has had the time to figure out if the migration would be clean then update all of our auto-testing infrastructure (which itself is over a decade old) to use git, all while not stopping active development.
You can use a git client to connect to SVN repo, which is really neat if you have to deal with a SVN repo. Therefore I would assume git has no issues with migrating the history from SVN.
Only for repos where there are no code reviews or releases. E.g small single developer utilities, configuration repos, etc.
Were there at least tests (where possible) if there were no code reviews?